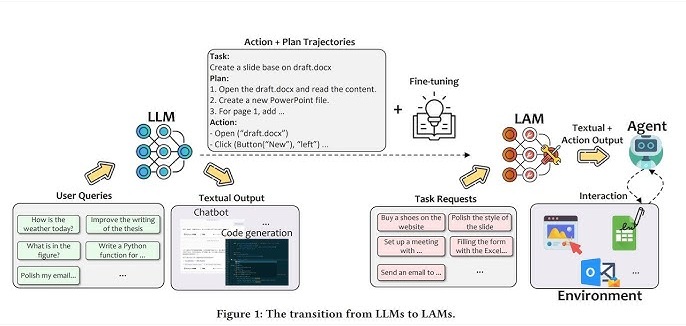
Introduction
In this comprehensive episode, delve deep into the transformative potential of Large Action Models (LAMs) and their pivotal significance for enterprise executives. Through detailed analysis and real-world examples, the discussion thoroughly examines how LAMs serve as a crucial bridge between sophisticated language models and concrete real-world actions. This exploration provides CxOs with valuable, practical insights and strategic considerations for successful technology implementation in their organizations. The conversation highlights both the immediate applications and long-term implications of integrating LAMs into enterprise operations.
About Large Action Models (LAMs)
Large Action Models (LAMs) are a groundbreaking development in artificial intelligence, offering enterprises the potential to automate complex tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance customer experiences. Here’s a comprehensive overview of LAMs, including their implications for enterprises, installation, configuration, and application design.
What are Large Action Models (LAMs)?
LAMs are AI models that can understand human intentions and translate them into actions within a given environment or system. Unlike traditional machine learning models that focus on pattern recognition or static predictions, LAMs are designed to take concrete actions based on their understanding of human input and the context of their operating environment.
Implications for Enterprises
LAMs have the potential to revolutionize various aspects of enterprise operations, including:
- Automation: Automating complex tasks, such as customer service, data entry, and supply chain management, can significantly improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Decision-making: LAMs can analyze vast amounts of data to provide insights and recommendations for better decision-making in areas like finance, marketing, and operations.
- Customer experience: By understanding customer needs and preferences, LAMs can personalize interactions and provide more efficient and effective support.
- Innovation: LAMs can be used to develop new products and services, identify new market opportunities, and optimize existing processes.
Installation, Configuration, and Design
Implementing LAMs in an enterprise setting requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- Data Preparation:
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, such as customer interactions, business transactions, and internal systems.
- Data Cleaning: Ensure data quality by cleaning, preprocessing, and transforming data into a suitable format for the LAM.
- Data Enrichment: Enhance data with additional information to improve model accuracy and insights.
- Model Selection and Training:
- Model Selection: Choose the appropriate LAM architecture based on the specific use case and available data.
- Model Training: Train the model on the prepared data using advanced techniques like reinforcement learning and deep learning.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Fine-tune the model’s parameters to optimize performance.
- Integration and Deployment:
- Integration: Integrate the trained model with existing enterprise systems and applications.
- Deployment: Deploy the model in a production environment, ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the model’s performance and identify any issues or biases.
- Maintenance: Regularly update and retrain the model to maintain accuracy and adapt to changing business needs.
Designing LAM Applications
When designing LAM applications, consider the following factors:
- User Interface: Create a user-friendly interface that allows users to interact with the LAM in a natural and intuitive way.
- Action Space: Define the range of actions that the LAM can take, ensuring that they are relevant to the specific use case.
- Reward Function: Design a reward function that incentivizes the LAM to take actions that are beneficial to the enterprise.
- Safety and Ethics: Implement safeguards to ensure that the LAM operates safely and ethically, avoiding biases and unintended consequences.
Video about LAM:
Key Sections of the Video
Understanding LAMs
- LAMs extend beyond traditional large language models (LLMs) by executing actions rather than just generating text
- They combine language processing capabilities with operational functionality
- Can interact with enterprise systems, APIs, and physical hardware
- Enables automation of complex, multi-step tasks across different platforms
Technical Architecture
- Built on LLM foundation with additional agentic frameworks
- Includes specialized training on task-action datasets
- Features environment integration layers for real-world interaction
- Incorporates feedback loops and adaptive learning capabilities
Practical Applications
- HR processes: Resume scanning, candidate ranking, interview scheduling
- Supply chain: Inventory monitoring, purchase order generation, vendor communication
- Marketing: Performance reporting, campaign analysis, presentation creation
- IT Operations: Server monitoring, resource management, infrastructure scaling
Implementation Strategy
- Start with well-defined pilot projects
- Focus on high-volume, stable processes
- Ensure proper data preparation and environment integration
- Implement robust testing and evaluation procedures
- Scale gradually with careful monitoring
Safety and Risk Management
- Implement tiered autonomy systems
- Establish clear permission structures
- Maintain comprehensive audit trails
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements
- Monitor and log all actions for accountability
Organizational Considerations
- Culture change management is crucial
- Need for clear communication about AI’s role
- Focus on employee empowerment rather than replacement
- Requirement for new skill sets and training programs
- Importance of cross-departmental coordination
LAMs Can help to improve Enterprise performance in 5 years
Large Action Models (LAMs) have the potential to significantly improve company performance over the next 5 years. Here are some key ways enterprises can leverage LAMs:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
- Hyper-personalized interactions: LAMs can analyze customer data to tailor experiences, from product recommendations to personalized support.
- 24/7 accessible support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant support, freeing up human agents for complex issues.
- Proactive issue resolution: LAMs can predict potential problems and proactively address them, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Operational Efficiency
- Automation of repetitive tasks: Automating tasks like data entry, scheduling, and report generation can free up employees for more strategic work.
- Supply chain optimization: LAMs can analyze market trends, predict demand, and optimize inventory levels, reducing costs and minimizing disruptions.
- Improved decision-making: By analyzing vast amounts of data, LAMs can provide valuable insights for better decision-making in areas like finance, marketing, and operations.
3. Product Innovation
- Accelerated research and development: LAMs can assist in research, analyze scientific literature, and generate new ideas, speeding up the innovation process.
- Personalized product development: LAMs can analyze customer feedback and preferences to create products that better meet their needs.
- Enhanced product design: AI-powered tools can assist in product design, prototyping, and testing, improving product quality and time-to-market.
4. Competitive Advantage
- Data-driven insights: By leveraging LAMs to analyze data, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, competitors, and market trends.
- Increased productivity: Automating tasks and improving decision-making can lead to significant increases in productivity and efficiency.
- New revenue streams: LAMs can be used to develop new products and services, creating new revenue streams and expanding market reach.
Conclusion
Large Action Models are a powerful tool for enterprises looking to leverage AI to improve efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences. By carefully planning and implementing LAMs, organizations can unlock new opportunities and gain a competitive advantage in the digital age.
By embracing LAMs and strategically integrating them into their operations, enterprises can unlock significant value, improve performance, and gain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving business landscape.
By understanding the capabilities and limitations of LAMs, enterprises can effectively harness their potential to drive innovation and achieve business goals.
Key Considerations
- Data quality: The accuracy and effectiveness of LAMs depend heavily on the quality of the data they are trained on.
- Ethical considerations: It’s important to consider ethical implications, such as bias and fairness, when developing and deploying LAMs.
- Continuous learning: LAMs need to be continuously trained and updated to maintain accuracy and adapt to changing business needs.
Key Takeaways
- LAMs represent a significant evolution from traditional LLMs by enabling direct action execution
- Success requires careful planning, robust data preparation, and strong governance frameworks
- Implementation should be gradual and focused on specific use cases with clear ROI
- Organizations must balance automation potential with safety and reliability concerns
- Cultural transformation and employee buy-in are critical success factors
Expert Insights
- Shimmer: Emphasizes the importance of data readiness and strategic vision
- Shri: Focuses on technical architecture and safety considerations
- Venus: Highlights practical applications and organizational impact
Related References
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integration with AI
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms with AI
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) with AI
- App AI Agent framework
- HIPAA guidelines for healthcare applications
- Financial regulatory compliance AI frameworks
- Stanford University Human-Centered AI


