Introduction:
The video introduces the exciting prospect of leveraging Large Language Model (LLM) integration in various business contexts. Zen, a seasoned software engineer at GitHub, provides valuable insights into the intricacies of developing and implementing practical LLM features tailored to meet organizations’ specific needs. Through a compelling case study on GitHub’s Co-pilot and GI Up Support, Zen vividly demonstrates the immense value of harnessing LLM technology in the business landscape. The case study illustrates how integrating LLMs can revolutionize self-help mechanisms in customer interactions, effectively addressing the evolving demands and challenges faced by organizations in today’s competitive market.
Large Language Models (LLMs) Integration:
LLMs are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, and their potential for business applications is vast. This topic delves into both the technical aspects of LLM integration and the practical considerations for implementing them in real-world business scenarios.
Technical Overview:
- What are LLMs? LLMs are advanced AI models trained on massive datasets of text and code. They can understand and generate human-like language, perform various tasks like translation, writing different kinds of creative content, and answering your questions in an informative way.
- How do they work? LLMs use complex algorithms like transformers to analyze relationships between words and sentences, allowing them to grasp language context and generate meaningful responses. They learn from the data they are trained on, continuously improving their performance.
- Integration methods: Integrating LLMs into your business systems can involve various approaches, such as:
- API access: Many LLM providers offer APIs that allow businesses to integrate their models into existing applications.
- Containerization: Deploying LLMs as containers allows for easier scaling and management within your infrastructure.
- Custom development: For specific needs, businesses can develop custom applications and interfaces to leverage the capabilities of LLMs.
Implementation in Business Contexts:
- Identifying use cases: The key to successful LLM integration is finding the right use case within your business operations. Consider areas like:
- Customer support: LLMs can analyze customer data and provide personalized support, answer FAQs, and even draft responses to inquiries.
- Content creation: Generate marketing materials, product descriptions, and blog posts, or even personalize content for individual users.
- Data analysis: Extract insights from large datasets, summarize documents, and identify trends.
- Software development: Assist with code generation, bug detection, and documentation writing.
- Data preparation and fine-tuning: LLMs require high-quality, relevant data to perform optimally. Gathering and preparing domain-specific data is crucial for accurate results. Fine-tuning the model on your specific data can further enhance its performance.
- Integration with existing systems: Seamless integration with your existing workflows and infrastructure is essential for successful LLM implementation. Consider factors like API compatibility, data security, and user interface design.
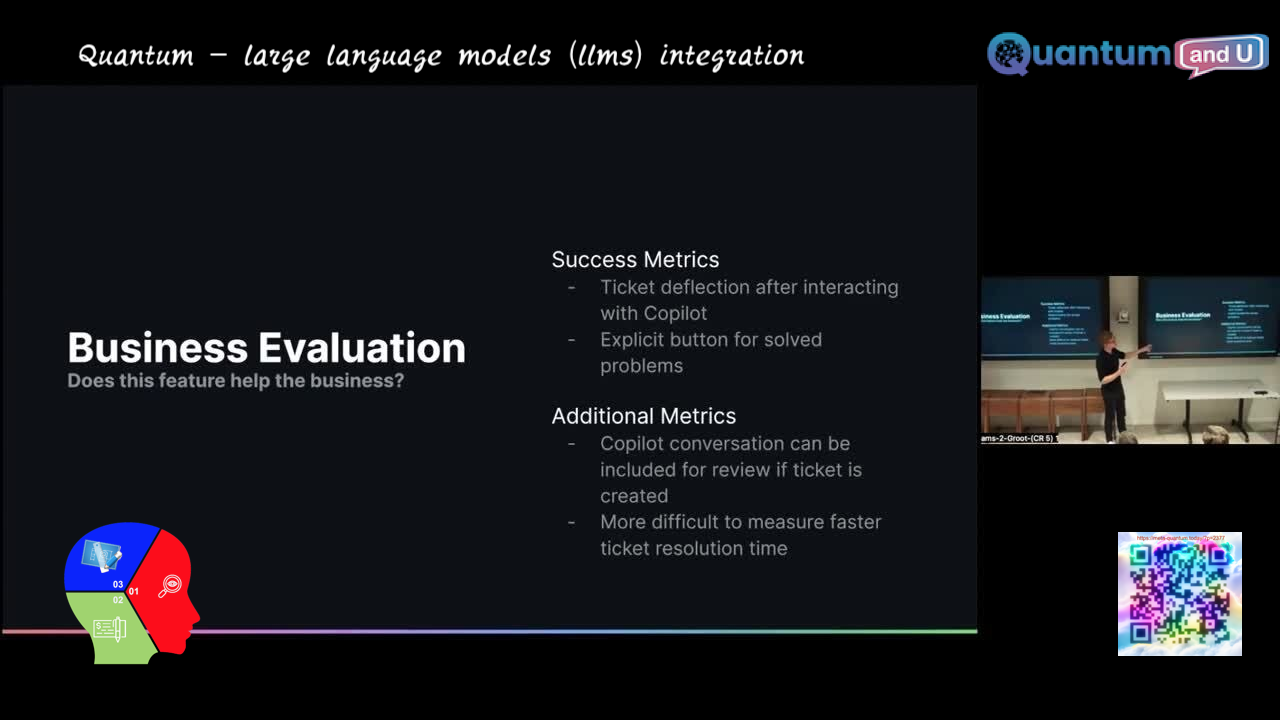
- Monitoring and evaluation: Continuously monitor the performance of your LLM system and track metrics like accuracy, response time, and user satisfaction. This allows for ongoing improvement and optimization.
Watch the Video about LLMs Integration:
Related Sections about the video:
- Business Context and Support Portal:
- GitHub’s self-help approach and the importance of customer-driven solutions.
- Overview of the GitHub Support Portal, a platform for coding discussions and issue resolutions.
- Co-pilot and GI Up Support Solution:
- Transformation of GitHub Co-pilot from an extension to a more versatile tool.
- Integration of Co-pilot in pull requests and its expanded functionalities.
- Microsoft’s implementation of Co-pilot in their suite of products.
- Technical Details and Implementation Timeline:
- A walkthrough of the GitHub Support Portal’s project roadmap, dating back to March 2023.
- Discussion on the significance of March 2023 and the inception of the project.
- Ensuring Responsible AI:
- Challenges in measuring success and the need to address real business issues.
- Consideration of responsible AI practices, including red team testing and simulation.
- Quality Data and Validation Process:
- The importance of high-quality data and reliance on GitHub documentation.
- Validation process involving support engineers to ensure accurate and useful responses.
- User Safety and Reducing Irreversible Effects:
- Challenges in dealing with potential irreversible actions suggested by Co-pilot.
- The red team test to ensure responsible AI and avoid unintended consequences.
- Continuous Improvement and Communication:
- Ongoing efforts to improve the system and handle complex queries.
- Strategies for communicating details about the solution within GitHub.
Impact of Large Language Models (LLMs) Integration in SEA:
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Southeast Asia is poised to have a significant impact on various sectors, including:
- Customer service: LLMs can be used to automate customer service tasks such as answering frequently asked questions, providing product information, and resolving simple issues. This can free up human agents to handle more complex inquiries and improve overall customer satisfaction.
- Content creation: LLMs can be used to generate creative text formats, like poems, code, scripts, musical pieces, email, letters, etc., which can be helpful for marketing and advertising campaigns, as well as for creating educational materials and training documents.
- Machine translation: LLMs can be used to translate text between languages more accurately and fluently than traditional machine translation methods. This can be helpful for businesses operating in multiple countries or regions.
- Data analysis: LLMs can be used to analyze large amounts of text data to identify trends and patterns. This can be helpful for businesses in a variety of industries, such as finance, healthcare, and retail.
LLMs Market in SEA:
The market size for LLMs in Southeast Asia is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market for LLMs is expected to reach USD 28.61 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.2%. The Southeast Asian market is expected to be one of the fastest-growing regions for LLMs, due to factors such as increasing internet penetration, rising disposable incomes, and a growing demand for AI-powered solutions.
The factors that are driving the growth of the LLM market in Southeast Asia:
- Government support: Several governments in Southeast Asia are investing in AI research and development, which is helping to create a more supportive ecosystem for LLMs.
- Growing tech startup scene: Southeast Asia has a thriving tech startup scene, which is creating a demand for innovative AI solutions, including LLMs.
- Increasing awareness of LLMs: More businesses in Southeast Asia are becoming aware of the potential benefits of LLMs, which is leading to increased adoption.
Conclusion:
The integration of Language Model Models (LLMs) is expected to bring positive changes to the Southeast Asian economy, creating new job opportunities, enhancing productivity, and improving efficiency. These advancements can revolutionize sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and customer service. However, it is important to acknowledge potential challenges. One major concern is job displacement as LLMs become capable of autonomously performing tasks previously done by humans. This could lead to unemployment and upheaval in the job market. To address this, reskilling and upskilling the workforce is crucial to adapt to the changing job landscape. Another challenge is the potential for bias in LLMs, as they may learn and perpetuate biases from their training data. Regular auditing and reviewing of training data can help mitigate biases. Involving diverse teams in LLM development can ensure a more inclusive and unbiased approach. Security is also a vital concern. LLMs are complex and vulnerable to attacks, so robust security measures such as encryption, vulnerability testing, and privacy regulations should be implemented to safeguard sensitive information and important decisions. In conclusion, while integrating LLMs holds promise for the Southeast Asian economy, it is important to address potential challenges. By focusing on reskilling and upskilling, combating bias, and ensuring robust security measures, LLMs can be utilized responsibly and ethically to maximize their positive impact. Through careful consideration and proactive measures, the Southeast Asian region can harness the full potential of LLMs while ensuring a prosperous and inclusive future.
Takeaway Key Points:
- High-quality data is fundamental for LLM success.
- Responsible AI practices are crucial for implementation and user safety.
- Continuous improvement and communication are vital for adapting to evolving business needs.
References:
- GitHub Co-pilot features.
- Microsoft’s new implementation of Co-pilot guide.
- LLMs for Business Leaders: A comprehensive Guide
I hope this overview provides a starting point for understanding LLM integration and its potential for your business. If you have any specific questions or want to delve deeper into a particular aspect, feel free to ask!


